Are you looking for a cost-effective, sustainable solution to protect your print and packaging? Aqueous coating offers the perfect solution. This popular finishing technique helps your product stand out in a competitive market while protecting it from scratches and fingerprint marks.
In this blog, we’ll discuss the aqueous coating process, its applications, benefits, and limitations. We’ll also compare it with other popular coating techniques and tell you how to choose the right type of coating for any base material (commonly known as substrate).
What is Aqueous Coating?
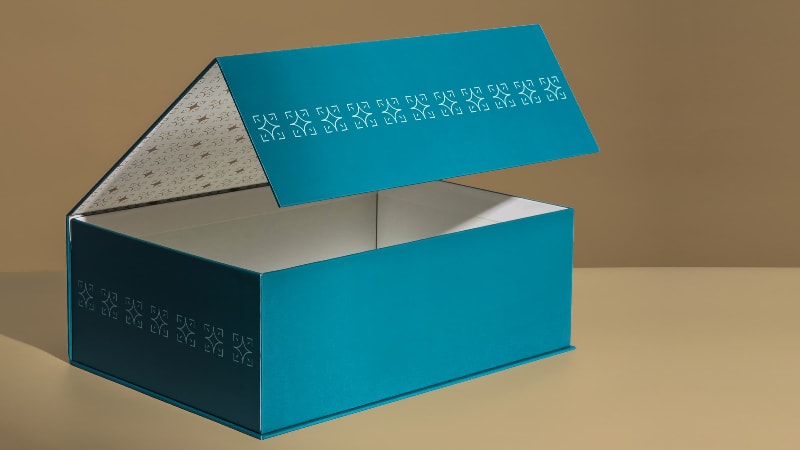
Have you ever wondered why some materials look glossy while others feel matte and subtle? That’s the result of an aqueous finish. Aqueous coating (AQ coating) refers to the process of applying a clear, water-based protective finish to packaging and printed materials.
This coating preserves the printed materials from fingerprints, scratches, etc., and makes the designs stand out by giving them a clean, professional look. It consists of water, polymers, wax, preservatives, and additives for durability and gloss. The primary ingredient is water. Polymers create the thin film on the substrate, and wax is added for its anti-scuff properties.
Aqueous coatings come in various types, each designed to achieve a specific finish and appearance. Below are six common types of aqueous coatings.
1. Gloss Aqueous Coating
Gloss coating produces a less shiny, more muted finish than UV or varnish coating. It is a clear coating with a reflective, glossy finish and smooth surface. Glossy coatings are commonly used for brochures, catalogs, and business cards.

2. Matte Aqueous Coating
Matte coating is similar to gloss coating except that it offers a non-reflective finish with reduced glare. It is ideal for applications that require protection with a more subtle, sophisticated look. Matte coating minimizes glossiness and is often used for luxury packaging, art books, and high-end publications.
3. Satin Aqueous Coating
A satin coating is a compromise between gloss and matte coating. It offers a semi-gloss finish with minimal shine and depth but great protection against fingerprints and blemishes. Common applications include annual reports, brochures, etc.
4. Dry Erase Aqueous Coating
The next type of aqueous coating on the list is dry-erase coating, which gives a smooth, highly-glossy effect like lamination.
However, lamination is more expensive, so if you want a high-gloss finish on a budget, dry-erase coating is the perfect affordable alternative to lamination. Popular use cases include packaging, magazines, and promotional materials.

5. Pencil-Receptive Aqueous Coating
Pencil-receptive aqueous coating is a special type of coating specifically designed to allow pencil, ink, or laser drawings on the coated surface. Although it is possible to write on some of the other coating types, writing may result in smudging or erasing afterward. Some typical applications include notebooks, journals, and custom packaging.
6. Soft-Touch Aqueous Coating
Soft-touch coatings have a smooth, velvety texture that adds a unique, high-end feel to the product. The finish is very similar to matte coating, giving it a subtle look with less shine. Soft-touch coatings are commonly used for premium packaging, luxury products, and high-end marketing materials.
How is Aqueous Coating Applied to Product Packaging?
Aqueous coating is the final step in the printing process. Once the print is transferred to the paper, a special machine with rollers coats the surface of the printed paper with a thin, even layer. The coating brings out the richness of the printed colors, making them stand out.
Generally, there are two common methods for coating any substrate surface: flood coating (uniform coating on the entire sheet) and spot coating (coating selective areas). However, aqueous coating is applied only as a flood coating, which makes the process more efficient for large print runs, resulting in a cost-efficient finish.

Once the press sheet is coated, it is passed onto a heated system to dry rapidly. The final product then goes through some additional finishing steps, such as cutting, gluing, and embossing or debossing.
Other Common Types of Finishes: UV Coating and Varnishing
Aside from aqueous coating, two other popular finishing techniques are UV coating and varnishing. Let’s discuss each of them briefly.
UV Coating
UV coating (or Ultra Violet coating) is a finishing process in which a clear liquid compound is applied to the printed surface and then cured using UV light. This turns the liquid components into solids instantly, giving a high-gloss finish.
The drying process is one of the main differences between aqueous coating and UV coating. UV coating is only used when a high-quality finish is required.
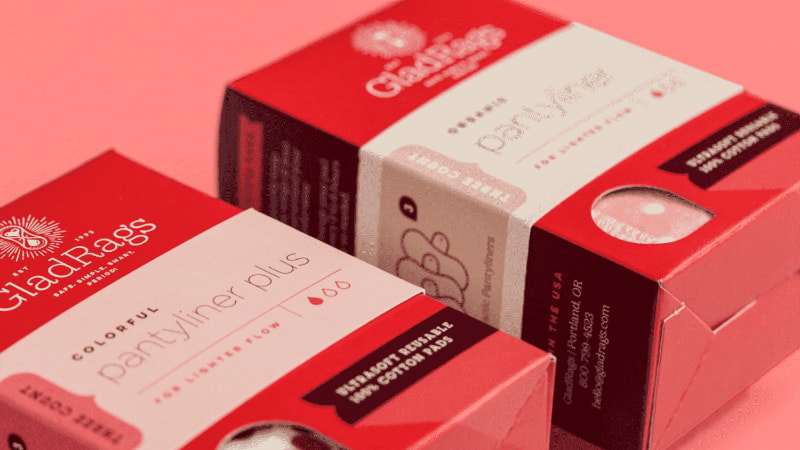

Varnishing
Varnishing is a finishing technique used to apply a resin, oil, or solvent-based coating to the surface of a substrate. Varnish coatings give a transparent liquid coating across the surface, making it look like it pops off the page more. It offers multiple options, like a matte or dull varnish or a gloss varnish.
Aqueous Coating vs. UV Coating vs. Varnish: Which is Best?
All three types of coating, aqueous, UV, and varnishing, offer similar features. Each provides protection against scratches and fingerprints, enhances the appearance, and increases the durability of the printed material. However, these differ significantly in various factors, including composition, cost, and drying speed.
Here’s a detailed comparison between aqueous coating, UV coating, and varnishing to help you choose the right type of finish for your next print project or packaging.
| Feature | Aqueous Coating | UV Coating | Varnishing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Water-based coating | UV-reactive liquid coating | Resin, oil or solvent-based coating |
| Coating Area | Flood coating only | Flood or spot coating | Flood or spot coating |
| Finish | Soft, subtle finish with minimal glare | Extremely shiny and reflective | Subtle to moderately glossy, depending on the type |
| Drying Process | Dries as water evaporates | Curation under UV light | Air-dried or heat-dried |
| Drying Speed | Moderate to fast | Fastest | Slowest |
| Durability | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly | Not eco-friendly | Depends on type |
| Cost | Cost-effective | Expensive | Depends on type |
| Discoloration (Yellowing over time) | Less prone to yellowing | Does not yellow | More prone to yellowing |
7 Key Benefits of Aqueous Coating for Packaging
Now that you are familiar with all the basics of aqueous coating, let’s discuss some of the pros of aqueous coating in packaging & printing.

1. Versatile Solution
Since aqueous coatings offer various types of finishes, such as gloss, matte, satin, soft-touch, etc., they are suitable for many applications and compatible with various substrates, including paper and cardboard.
2. Improved Durability
An aqueous coating protects the surface from scratches, sticky fingers, scuffs, and abrasions. It also offers resistance against moisture and dust, making it ideal for packaging and printed materials.
3. Light on the Pocket
AQ coating is a budget-friendly option compared to UV coating or other specialized options. Its affordability makes it accessible for large-scale production runs, and its short drying time boosts the efficiency of the coating process for printing, reducing labor costs and production delays.
4. Eco-Friendly Alternative
Unlike UV coating, aqueous coating comprises a non-toxic water-based solution with fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Packaging design with aqueous coating reduces harmful emissions during the application, making it a sustainable choice and safer to handle during the printing and finishing process.

5. Variation in Styles
Aqueous coatings are used across various industries based on each sector’s needs. They come in different styles that allow different color models, especially CMYK or Pantone colors, that truly appear vibrant.
6. Less Likely to Get Yellow
UV coatings can degrade upon exposure to light, heat, and air, resulting in a yellowish tint. However, due to the very few VOCs in their composition, water-based coatings are less likely to face yellowing. This feature makes them ideal for preserving the visual integrity of printed materials and packaging.
7. Fast Drying Speed
Water-based coatings dry as the water evaporates. During the printing process, when the coated surface is passed through the heated system and exposed to heated air, it dries very quickly. This increases efficiency and makes them a valuable option for high-volume printing projects where quick turnaround times are important.
What are the Limitations of Aqueous Coating?
While aqueous coatings offer numerous benefits, there are some downsides that you should be aware of.

1. Limited Durability
Although water-based coatings provide basic protection against scuffing and moisture, they are less durable than UV-reactive coatings. This makes aqueous coatings more prone to damage when exposed to harsh conditions, poor handling, or rubbing.
2. Lower Gloss Levels
The gloss aqueous coating provides a reflective shine to the coated surface, but it’s still less than the shine we get from UV-reactive coatings. This feature makes AQ coatings unsuitable for applications requiring a very high-gloss, mirror-like finish.
3. Only available as a Flood Coating
Aqueous coating is only applicable as a flood coating, meaning it covers the entire surface of the printed material uniformly, rather than being able to be applied to selective areas. This characteristic makes it unsuitable for spot coating applications where only certain parts of a design, such as a logo or some other element, require a glossy or matte finish.
4. Blocking
Blocking refers to the sticking of coated surfaces with each other due to heat, pressure, or humidity, making it difficult to separate them without damage. It is a prevalent issue in aqueous coating. Blocking occurs when printed or coated materials are handled, transported, or stacked immediately after production.

5. Setoff
Another commonly faced issue in aqueous coating is setoff. It refers to the transfer of wet ink from one surface to another. Aqueous coatings are often used in printing processes to help protect the freshly printed ink while it dries. However, if the ink is not fully oxidized and dried, it can transfer to another adjacent surface when stacked.
5 Best Use Cases For Aqueous Coating
Due to its versatility, eco-friendliness, cost-effectiveness, and durability, aqueous coatings are widely used in the packaging and printing industries. The global market for water-based coatings is projected to reach over $3.8 billion by 2032. Here are the five best use cases for aqueous coatings:
1. Food Packaging
Aqueous coatings are commonly used for food packaging as they are non-toxic, safe, and moisture-resistant. This is primarily due to the safety concerns in the food and health industry.
2. Retail Packaging
AQ coatings are also very popular in the retail packaging industry. They make the colors appear more vibrant, making the product stand out while protecting it against environmental threats.

3. Commercial Printing
AQ coatings are often applied to brochures, catalogs, business cards, and flyers to give them a subtle glossy finish. This makes the brand appear more professional and gives it a premium feel.
4. Household products
This type of coating is commonly used for household products such as consumer electronics, food and beverage labels, cleaning product bottles, etc. The coatings increase the product’s visual appeal and resist smudging and moisture damage.
5. Book and Magazine Covers
AQ coatings are often used on the covers of books and magazines. This improves the shelf life of the printed material, makes it eye-catching, and resists any fading or damage to the print.
How to Choose the Right Coating Type for Your Packaging?
Choosing the right coating type for your project can feel overwhelming because of the number of available options. Here are a few things to consider while choosing the coating type for your packaging or print project:

- Substrate: Aqueous coatings work well for paper and cardboard and are durable. However, for metal or plastic surfaces, UV-coating or lamination may give better results.
- Finish: Think about how you want your final product to look. Should it be super glossy, semi-glossy, or matte? If you want a super-gloss finish, UV coating is a better choice than water-based coating, as the latter offers lower gloss levels.
- Level of Protection: Decide what the required level of protection for your product is. If it’s highly sensitive, opt for UV coating or varnishing. However, if medium protection is required, go for an aqueous coating.
- Budget: Check your budget. Aqueous coating is a cheaper alternative than other specialized coatings, so if you have a limited budget or no specialized equipment, go for aqueous coating.

- Testing: Always test the coating on the packaging material you wish to get coated. Ensure compatibility and your desired level of protection before committing to bigger production.
- Environment: If you are an environmentally conscious business owner, aqueous coating is an ideal choice. You can advertise your packaging as eco-friendly and attract customers who promote green living.
FAQs
Q1: Is aqueous coating recyclable?
Yes, aqueous coatings are generally recyclable because they are water-based, non-toxic, and eco-friendly. Coated paper is also easily recyclable and does not produce harmful by-products.
Q2: Can aqueous coating be used on all types of materials?
No, although aqueous coatings are versatile, they cannot be used on all types of materials. Although they are commonly used on paper and cardboard, they are not suitable for non-porous surfaces like plastic, metal, or glass.
Q3: Does aqueous coating add to printing costs significantly?
The aqueous coating adds to printing costs, but not significantly, as it does not need a special UV light, and it is applied in-line. It is cheaper than UV coating or lamination.
Q4: Is aqueous coating waterproof?
Aqueous coating is water-based; however, it’s not fully waterproof. It can resist moisture to some extent, but it cannot withstand prolonged exposure to water. Acrylic varnishing can provide decent waterproofing.
Conclusion
In this detailed guide, we explained aqueous coating, its application process, and its merits and demerits. We also reviewed other common finishing techniques and their differences.
Now that you understand the importance of aqueous coatings for packaging and printing and their compatibility with various materials, you are well-equipped to decide if they are the right choice for your next project.
Get the Best Packaging with Aqueous Coating at Packoi
Looking for a supplier to buy marketing materials, display boxes, gift boxes, and shipping boxes? Packoi has established itself as the leading supplier of top-quality packaging solutions. Contact us today.




