Last Updated on January 7, 2025 by Packoi Team
Are you confused about measuring cardboard thickness and what size suits your needs? Your purpose decides what thickness you should consider, whether it’s about shipping boxes or creative crafts. Thickness affects strength and suitability for each use. This guide will help you measure thickness, understand the types, and find the perfect fit for your needs. Let’s dive in!
What is Cardboard Thickness?
Cardboard thickness is the depth of cardboard measured in millimeters or microns. Thickness determines the durability, resilience and strength of the material, hence plays a key role in packaging. Thicker cardboard gives better protection but also adds to weight and cost. A caliper or micrometer is used to measure the cardboard thickness accurately.
The weight is not the same as the thickness of cardboard. Thickness is a measure of depth, and weight is a measure of mass, usually expressed in pounds per square foot or grams per square meter (GSM). A thin cardboard sheet may weigh more if it’s made from denser material. This difference is vital when choosing materials for packaging or construction to balance strength and weight.
Factors Affecting Thickness

The type of cardboard and how it’s made has a huge effect on thickness. Corrugated cardboard is thicker than flat paperboard and has sheets of fluted paper sandwiched in between. The different combinations of flute sizes— from micro-flutes to heavy-duty types — create depth and cushioning. Thickness increases with more layers, and so does stiffness.
Materials that are used to make cardboard also matter. There may be more variation in the thickness of recycled paperboard versus virgin fibers. Overall performance is determined by flute type and thickness in combination with the quality of the paperboard. For instance, E-flutes are thinner, compact sheets that offer great cushioning for smaller boxes, whereas C-flutes are for thicker boxes designed for shipping containers. Knowing these factors will help you choose the right cardboard for your specific needs — without unnecessary bulk but still durable.
How to Measure Cardboard Thickness
Cardboard thickness can be measured in a few different units:
- Points
- Inches
- Millimetres
- GSM

Points
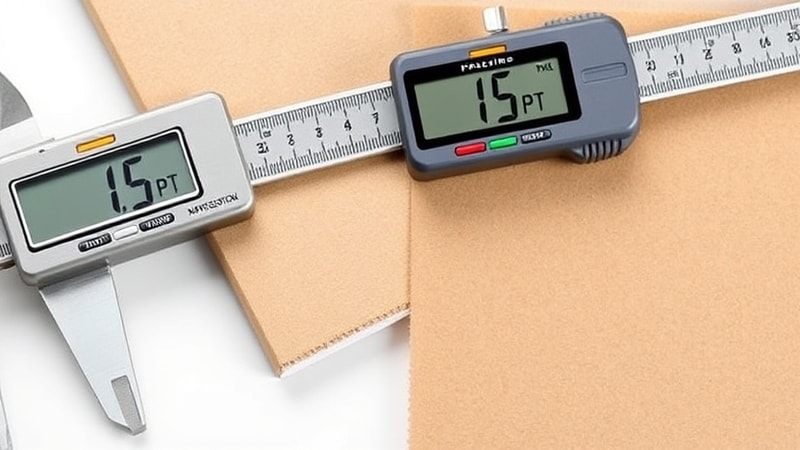
The unit “Point,” symbolized as Pt, is widely used in commercial and industrial sectors to measure material thickness. It is particularly common in industries dealing with paper, cardboard, and similar objects. One Pt equals 0.001 inches, making it a precise and convenient unit. For instance, if a cardboard is 15 Pt thick, its thickness would translate to 0.015 inches or approximately 0.38 mm. This makes points a useful unit for applications requiring fine measurements.
Inches
Inches are another common unit for those measuring cardboard thickness, especially in the United States and other regions that use imperial measurements. When using a ruler, you’ll notice that one side often displays millimeters while the other side shows inches. Cardboard with a thickness of 0.38 mm equals 0.015 inches. This conversion is crucial when working in industries that need precise measurements in multiple-unit systems.
Millimeters
Millimeters (mm) are a standard unit for measuring thickness globally. They are especially useful for finer measurements in industries like packaging and printing. To measure in millimeters, you can use tools like a caliper or apply the simple stack-and-ruler method. This ensures accurate results without the need for advanced instruments.
GSM
GSM, or grams per square meter, measures the weight and thickness of paper-based packaging materials, including cardboard. A higher GSM indicates greater thickness and durability. For cardboard packaging, a high GSM in the range of 350-400 is often ideal, as it balances strength and usability. Understanding GSM helps in selecting the right material for packaging needs.
| Unit | Conversion |
|---|---|
| Points (Pt) | 1 Pt = 0.001 inches = 0.0254 mm |
| Inches | 1 inch = 25.4 mm = 1000 Pt |
| Millimeters | 1 mm = 0.03937 inches = 39.37 Pt |
| GSM | Higher GSM = Thicker cardboard |
Tools and Methods for Measuring Cardboard Thickness
Use these tools and two different methods to measure the cardboard thickness:
- Thickness Measuring Gauge
- Stack and Ruler Method
- Micrometer
- Caliper
Thickness Measuring Gauge
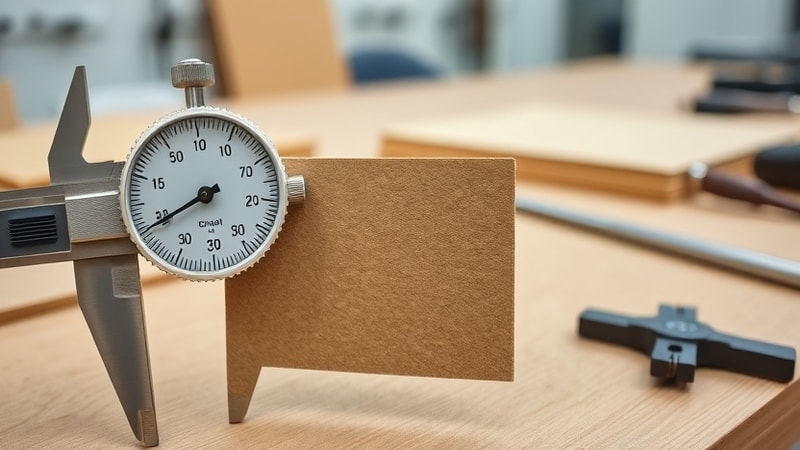
The thickness gauge is specially designed to check the thickness of paper-based materials like cardboard. It has two main parts: the spindle and the anvil. To use it, place the cardboard between these two parts and tighten them until the cardboard is securely held.
Once it’s in place, check the reading displayed on the gauge. This reading tells you the exact thickness of your cardboard. Use this information to decide if the material meets your packaging needs.
Stack and Ruler Method
The stack and ruler method is one of the simplest ways to find out cardboard thickness. All you need is a ruler and a few pieces of cardboard. Stack several pieces of cardboard together and measure the total thickness using the ruler.
Once you have the total measurement, divide it by the number of pieces in the stack. This gives you the thickness of each individual piece. It’s a quick and easy manual method to get accurate results.
Micrometer Screw Gauge
To measure with a micrometer, place the cardboard between the anvil and spindle. Turn the ratchet until the cardboard fits snugly. Once secured, read the thickness on the scale. This method ensures high accuracy for detailed measurements.
Caliper
A digital or dial caliper is another reliable tool. Place the cardboard between the jaws of the caliper and gently close them until the cardboard is held firmly. The thickness will be displayed on the caliper’s screen or dial.
Different Types of Cardboard and Their Thicknesses
Cardboard layers impact its thickness and strength, thus impacting its functionality. It is important to understand the types of cardboard, their layers, and varying thicknesses.
Understanding the Layers
The type of cardboard used affects its thickness and strength. Single-walled cardboard has one layer of fluting, making it lightweight and suitable for lighter items. Double-wall cardboard has two layers of fluting, providing more thickness and better durability for heavy or fragile goods. The extra, single-fluted layer in double-wall cardboard adds strength, ensuring items stay safe during the shipping process or storage. Choosing the right type depends on the weight and protection your items need.
Single-Wall Cardboard
Single-wall cardboard is a lightweight and strong material that consists of a single outer layer made of fluted paper sandwiched between two flat cardboard liners. Depending on the flute type and size, its thickness typically spans from 1/16 inch to 1/8 inch. The structure is perfect for light-duty boxes used in common shipping and packaging. Single-walled cardboard is a usual choice for shipping or storage of light weight goods such as books, clothing, and smaller electronics.
Double-Wall Cardboard
Double-wall cardboard has two layers of fluting and three flat liners for increased strength and durability. The thickness typically falls between 1/8 inches and 3/16 inches, meaning that it is a more heavy-duty option for shipping goods. Double-wall cardboard is used to pack delicate or heavier goods like ceramics, glassware, and parts of machinery. It is a go-to option for goods that need extra defense in transit or storage.
Triple-Wall Cardboard
Triple-wall cardboard contains three fluted layers and four flat liners for maximum strength. Usually, this type of cardboard is more than 3/16 inches thick and has an exceptional capacity to withstand load. It is mainly used for very heavy-duty packaging, e.g., bulk shipments of industrial materials or large, delicate items. It is an excellent option in rough shipping conditions.
Corrugated Cardboard vs. Paperboard

The fluted middle layer in the corrugated cardboard gives it greater cushioning and structural support than single-layer cardboard, making it perfect for shipping boxes. In contrast to corrugated cardboard, paperboard is a single-layer material that is thinner and more pliable. It’s ideally used for lightweight packaging such as cereal boxes, tissue boxes, or cosmetic packaging. Corrugated cardboard is strong, but paperboard is for aesthetic and lightweight applications.
Common Cardboard Thicknesses for Different Uses
Packaging Boxes
Sustainable Packaging boxes are usually made from cardboard with 32 ECT (Edge Crush Test) and 44 ECT ratings. These thicknesses are appropriate for use in shipping boxes because they are neither too thin nor too thick. For heavier weight or more sensitive items, you should opt for the cardboard of 200# test or 275# test strength. These are tough options that can take an additional burden during transit and stockpiling.
Cardboard Sheets for Crafts and DIY Projects
Cardboard sheets, which are used to make crafts and small home and DIY tasks, are comparatively thinner and may range from 1/16th inch to 1/8th inch in thickness. These sizes are light, and they can be easily cut, folded, or shaped in any desired way. They are suitable for creating models, decorations, or personalized packaging. Thin cardboard sheets are also ideal for schools or art-inspired projects since they give flexibility and stability.
Storage and Moving Boxes
Double-walled cardboard boxes are the most suitable option for stacked goods or transporting them. They have multiple layers that give the necessary rigidity and shield. These boxes typically have a 44 ECT rating or greater. This added thickness ensures robustness, especially when using it to pack items such as books, dishes, or tools. For lighter content, single-walled boxes with 32 ECT will do the job.
Choosing the Right Cardboard Thickness for Your Needs

Choosing the right cardboard thickness is critical for ensuring that your products are properly secured, whether for shipping, crafting, or heavy-duty use. The thickness of cardboard is critical in determining its durability, adaptability, and suitability for various applications. Understanding the specific cardboard required for different purposes can assist you in making the best decision for your specific needs.
Here is a detailed breakdown of all packaging solutions depending on industry needs.
Shipping and Packaging
Corrugated cardboard boxes are most commonly used in the shipping and packaging industry due to their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Most cardboard packaging boxes are made with multiple layers, including an inner liner, an outer liner, and a corrugated medium (the fluted paper between the layers). This multi-layer approach provides ideal protection to the package being shipped.
If your shipping situation is not as harsh or the product is not considered fragile, then single-wall corrugated sheets are ideal. Double-wall and triple-wall corrugated board options are better suited for heavier items.
If the package is highly fragile and requires maximum cushioning, then corrugated paper can be added as an inner packaging component. It adds a layer of protection, preventing items from shifting within the box and reducing the risk of damage.
Crafting and DIY Applications
Crafting projects and DIY applications require cardboard that is easy to cut, shape, and manipulate while maintaining structural integrity. Thin corrugated sheets with an F-flute or E-flute provide the versatility required for crafting. Such sheets are lightweight, easy to fold, and ideal for projects like creating custom gift boxes, decorations, or model-building materials.
However, if you want aesthetically pleasing results, then smooth corrugated paper or chipboard can be used on the outer layer. These materials are often used to create custom packaging where appearance matters just as much as functionality.
While these thin sheets are ideal for delicate craft projects, they are not suitable for large-scale DIY projects such as furniture prototypes or home decor items. In such situations, you must opt for double-wall corrugated sheets. Such cupboards are thick and provide the necessary strength for large-scale projects.
Heavy-Duty Applications
Only thick and durable packaging material can withstand the weight and pressure of heavy-duty applications. The double wall and triple wall corrugated board is designed to support the bulky and extra fragile items. It has additional layers of corrugated paper that provide superior protection against compression. It is ideal for packing appliances, machinery, or industrial components.
If you have a unique product, then you can always opt for a custom corrugated cardboard box designed to meet the dimensions and weight capacity of your product. Such customized packaging is necessary to reduce the risk of damage in heavy-duty applications.
If your product’s shipping condition is environmentally challenging, then you have to opt for weather-resistant corrugated sheets with added coatings or liners. Such options provide extra durability, protecting goods from moisture, temperature fluctuations, and other environmental factors.

Additional Considerations for Choosing Cardboard Thickness
Here are some additional factors to consider when choosing the ideal cardboard thickness for your business.
Cost vs. Performance
Balancing budget limits with performance expectations is crucial. While single-wall corrugated boxes are fine for standard shipments, high-value or heavy commodities should be shipped in double-wall or triple-wall containers for better protection
Testing and Certifications
Ensure that the cardboard meets industry specifications for weight-bearing capacity, burst strength, and edge crush resistance. These characteristics are especially important for transportation and heavy-duty applications.

Sustainability and Recyclability
Choose recyclable corrugated cardboard boxes or packaging with certifications demonstrating responsible sourcing. These choices help to reduce environmental effects and align with consumer demand for sustainable packaging.
Thick Cardboard vs. Thin Cardboard: Pros and Cons
| Feature | Thick Cardboard | Thin Cardboard |
|---|---|---|
| Pros | Stronger and more durable | Lightweight and easy to handle |
| Better protection for fragile items | Cost-effective for low-budget projects | |
| Provides structural support in packaging | Flexible and easy to cut and shape | |
| Can withstand heavy loads | Suitable for temporary uses or light items | |
| Cons | Heavier and bulkier | Less durable, may bend or tear easily |
| More expensive than thin cardboard | Provides less protection for fragile items | |
| Harder to cut and shape | Not ideal for heavy-duty or structural purposes | |
| Ideal Uses | Shipping heavy or fragile items | Packaging for light, non-fragile products |
| Structural support in construction | Temporary uses or disposable packaging | |
| Protection for electronics or delicate goods | Arts and crafts, small box-making |

Conclusion
The thickness of cardboard matters in packaging design. Choosing the right one can protect your products during transit, preventing damage. There are several ways to measure cardboard thickness, and selecting the right one is key.
For the best packaging results, consider seeking help from a packaging expert. They can assist in picking the perfect packaging for your brand, ensuring your customers are happy with their purchase.
Working with a Packaging Expert
While you have all the information about cardboard thickness, it’s still a good idea to consult a packaging expert. Our packaging experts have deep knowledge and can help you to choose the right packaging for your brand. Creating outstanding cardboard packaging is simple with the right guidance. Contact us to share your ideas so Packoi can help you create the perfect packaging.




